Sure, everyone knows that Google is a semantic search engine.
What this implies is…
Google makes an attempt to grasp the that means of your content material fairly than simply searching for literal key phrase matches.
The reason being that Google is trying to enhance the person expertise by trying to carry outcomes that extra precisely fulfill the searcher’s intent.
So as to do that Google has Pure Language Processing (NLP) algorithms that learn by your content material.
On this publish, I’ll try and reply:
- What’s pure language processing?
- How does pure language processing work?
- How do you utilize pure language processing in search engine optimisation?
To do that, I’ll be specializing in theoretical information in addition to placing on my scientist hat and doing somewhat experimentation. (Sure, I like tinkering.)
My purpose for this experiment is to have a deeper understanding of how you can use NLP in your semantic search engine optimisation technique.
However first, in case you had been questioning what Google’s NLP is…
What Is NLP (Pure Language Processing)?
NLP or pure language processing is a subject of synthetic intelligence that permits a machine to grasp human language, whether or not written or spoken. It’s a subject that mixes linguistics and laptop science permitting computer systems to investigate and ‘perceive’ language so as to extract that means from textual content and speech.
Now, you is likely to be questioning…
What’s Google’s pure language processing good for?
Pure language processing permits search engines like google and yahoo to carry surprisingly correct solutions to person queries and brings fast solutions to questions within the type of SERP options. It additionally helps the customers to refine their searches when the query is broad or obscure.
In different phrases, take into consideration this…
Have you ever observed that if you kind a question into Google, you get a surprisingly correct and related reply?
How does Google do it?
In actuality, Google solves two issues on the similar time.
First, Google has to grasp the question.
Give it some thought.
How do you phrase your question so that it’ll carry you the outcomes you might be truly searching for? For essentially the most half, you utilize pure language.
In distinction, assume again to the way you worded your question in 2018 earlier than Google’s BERT algorithm rolled out. From what I recall, you’d assemble a question based mostly on brief phrases. In case you didn’t discover what you had been searching for, you’d strive a number of variations till Google introduced the knowledge you had been searching for.
However, now, you kind a question utilizing pure language. Which means that Google has to grasp your question.
Secondly, as soon as Google understands your question, it has to determine what content material to carry so as to reply the query. This implies bringing a ranked listing of URLs in addition to SERP options.
To know which content material to carry you, Google wants to grasp the that means of the content material it has in its index.
This implies Pure Language Processing strategies analyze each the question and the content material in its index.
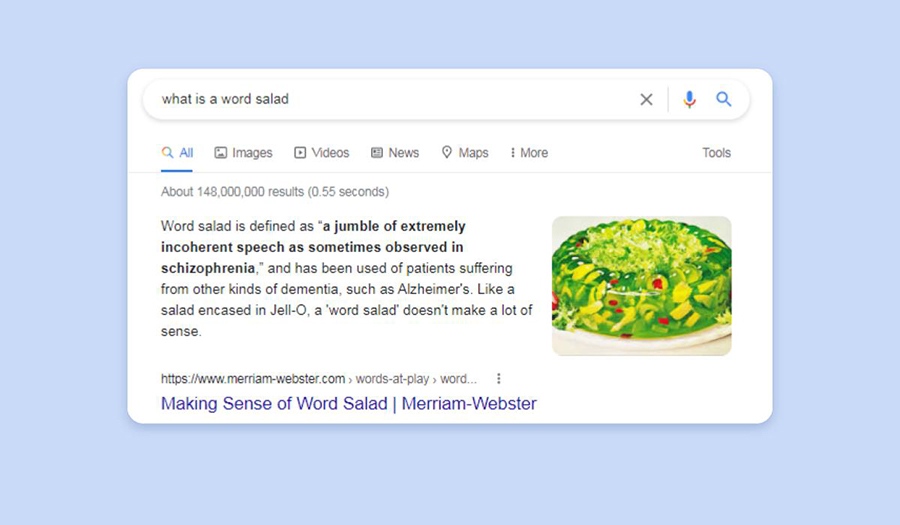
One of the best instance of that is within the content material included in Featured Snippets. When Featured Snippets had been new, they typically introduced incomprehensible phrase salads.
The reason being that Featured Snippets typically carry content material from unstructured paragraphs. This implies so as to present a easy and correct reply to a person question, Google has to do some modifying.
Now, as Google’s understanding of language has vastly improved over the previous couple of years, Featured Snippet textual content has turn into clear, helpful, and straightforward to grasp.
Lengthy gone are the times of the incomprehensible phrase salads as you possibly can see within the fairly ironic Featured Snippet under.
How Does Pure Language Processing Work?
Though it’s a giant topic, here’s a 30, 000 ft overview.
Google’s pure language processing algorithms work by dividing sentences up into completely different phrases, breaking the sentences down into elements of speech, and understanding the connection between phrases based mostly on grammar guidelines.
You’ll be able to simply see this for your self by analyzing your textual content with Google’s Pure Language API demo.




Subsequent Google identifies topics and objects as entities after which assigns them to entity varieties akin to particular person, location, group, and many others. The algorithms additionally determine recognized entities, which suggests entities that exist already in its information graph.
(As a aspect level, to really perceive this weblog publish, you want a transparent understanding of what entities and information graphs are. So, in case you had been questioning, I’ve included hyperlinks above to different weblog posts designed to make these ideas crystal clear.)
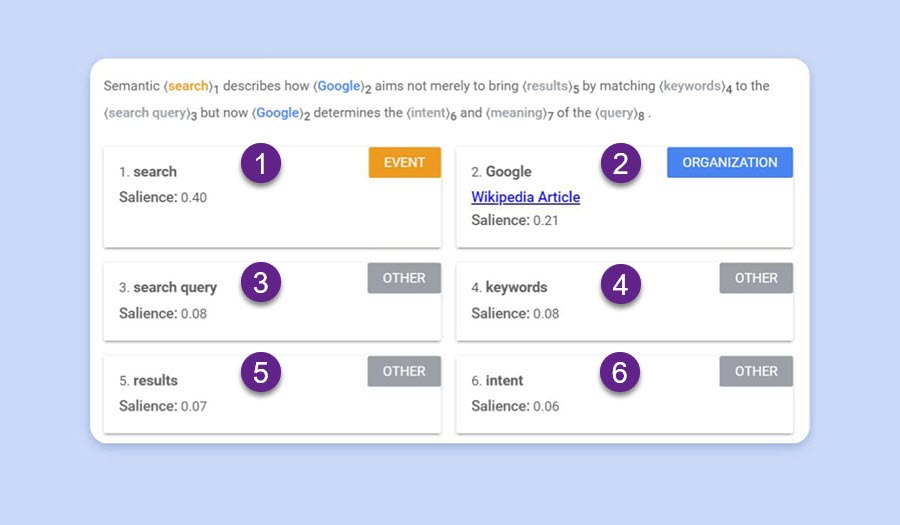



Google’s Pure Language API demo exhibiting how Google’s NLP breaks up sentences into entities.
Google additionally analyzes the sentiment, which suggests the angle that the author has towards the entities talked about within the textual content.




Google’s Pure Language API demo exhibiting Google’s NLP sentiment evaluation.
Google additionally makes an attempt to grasp the content material class. As you possibly can see within the screenshot under, the class of the analyzed textual content is Web & Telecom.




Okay, so now that you simply’ve had a glimpse into how Google understands content material, it turns into apparent that NLP and search engine optimisation go hand in hand.
So, let’s check out how Google understands language and see if we will glean some search engine optimisation insights.
4 Examples of NLP Based mostly on 4 Comparable Queries
To exhibit how Google’s NLP algorithms work, I created somewhat check to see how Google understands semantically comparable queries. What resulted are some nice examples of NLP.
On this experiment, my purpose is to grasp if Google understands the distinction between the queries. To do that I’ll look at:
- How Google solutions every question
- The semantics based mostly alone human understanding
- The semantics based mostly on Google’s NLP Demo instrument
Throughout this experiment, I particularly appeared for queries that carry Featured Snippet outcomes. I selected Featured Snippets as a result of, as I discussed above, so as to create one, Google typically brings varied parts collectively akin to textual content and pictures. How Google does that demonstrates how Google interprets every component.
And, since Google brings the Featured Snippet as a solution to the question, Featured Snippets additionally present how Google understands the question.
In different phrases, I needed to see how Google curates content material, which takes extra sophistication than simply bringing a listing of blue hyperlinks. As a result of the extra detailed the outcome, the much less doubtless Google took a wild fortunate guess.
I searched these 4 queries:
- What’s the Chinese language dragon image
- Dragon image Chinese language
- What’s the dragon image Chinese language
- What does the Chinese language dragon image characterize
Now, at a primary look, you may assume these queries have the identical or at the very least comparable intent.
And, if that’s the case, they need to all carry the identical outcomes.
So to check this out, I searched every one on Google.
And, as I’m certain you’ll think about, every outcome was completely different. What’s extra, they didn’t even carry the identical URLs, textual content, or photographs.
So let’s look at every one to attempt to perceive what Google sees and attempt to perceive why.
1. Instance #1 ‘What’s the Chinese language dragon image’
The primary question, ‘what’s the Chinese language dragon image’, is grammatically appropriate. In case you kind a question like this into Google you must in concept get the perfect outcomes.




As you possibly can see from the Featured Snippet above, Google brings a quote from Chineasy.com’s weblog publish entitled ‘The that means of the Dragon Image in Chinese language Tradition.’
Now earlier than taking a look at instruments, right here is my semantic evaluation based mostly alone human understanding. (Sure, my mind is my favourite search engine optimisation instrument.)
The question is worded to grasp what the Chinese language dragon image is. This implies the primary entity is the dragon image which comes from China.
Google solutions this query completely. As an example, the title tag expresses that the article will clarify the that means of the dragon image in Chinese language tradition. That is precisely what the searcher was searching for.



Wanting on the textual content within the Featured Snippet, you’ll discover that Google is explaining what dragons symbolize in Chinese language tradition.



Once more, it is a fairly good person expertise should you ask me. The Featured Snippet offers the person a fairly good overview of the subject.
Now, let’s bounce into Google’s Pure Language API demo to see how Google understands the question.
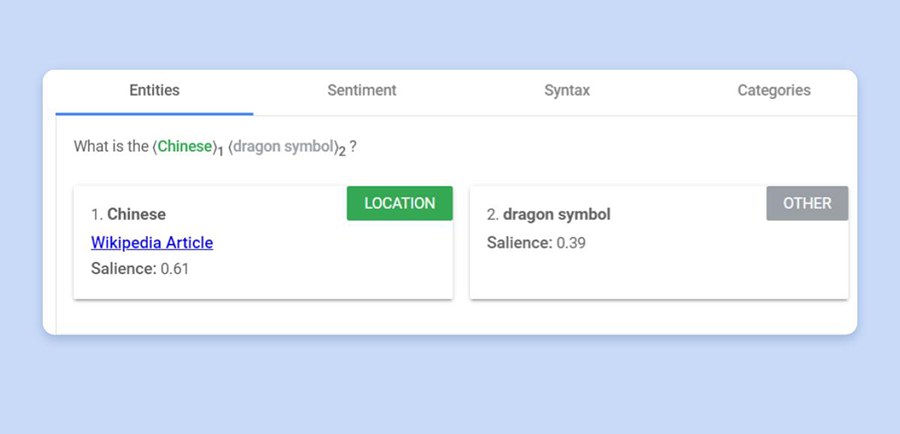



Wanting on the screenshot above, Google appears to grasp that there are two entities within the question.
Firstly, the phrase ‘Chinese language’ refers to China the placement. You’ll be able to see this by the truth that the API demo identifies it as ‘location’. Additionally, the instrument contains a hyperlink to a Wikipedia article about China. A Wikipedia article seems when Google acknowledges an entity that’s in its Information Graph.
In different phrases, Google acknowledges an unknown entity known as ‘dragon image’ and it’s associated to the placement ‘China’.
From my perspective, this traces up with my human understanding of the entities within the question and the result’s most probably to fulfill the person’s question.
Now let’s check out the following question.
2. Instance #2 – ‘Dragon image Chinese language’
The following question is ‘dragon image Chinese language’.
Regardless that this question shouldn’t be grammatically appropriate, as a human, I’d typically kind a question like this as short-hand for ‘What’s the Chinese language Dragon image?’
To me, the lacking ‘What’s the..’ is implied and the 2 queries imply the identical factor. My mind fills within the gaps.
However, to Google, the semantic variations require a wholly completely different reply.
Once I typed it into Google, that is what I noticed:




As you possibly can see within the screenshot above, Google presents data from Wikipedia.com. What occurred to the Chineasy.com URL that we noticed above?
If we go by the title tag alone, it looks as if Google is bringing content material from a basic article about Chinese language dragons fairly than a particular article that explains what the Chinese language dragon means in Chinese language tradition that we noticed when wanting on the earlier question.



Additionally, the content material within the Featured Snippet is somewhat awkward.



Though the reply is just like the one we noticed once we appeared on the earlier question, right here the primary sentence begins with ‘The dragon image can be…’. The phrase ‘additionally’ right here appears unusual.
So the massive questions are, why is the URL completely different, and why is the textual content awkward?
Maybe the reply is that the question is lacking the ‘What’s the…’ context phrases.
And, from expertise, when somebody varieties a broad time period into the search bar, Google offers a broad response that might fulfill plenty of person intents.
Simply surmising right here however, this may clarify why Google brings the Wikipedia article as a substitute of the Chineasy.com article.
The Wikipedia article is extra generic and doesn’t concentrate on the symbolism of the Chinese language dragon however covers the subject extra broadly.
It first explains what the Chinese language dragon is normally and solely mentions what it symbolizes within the fourth line.




And should you take a look at the screenshot above, you’ll see why the phrase ‘additionally’ is talked about within the Featured Snippet.
In different phrases, by the person excluding the phrases ‘What’s the…’, Google brings a extra generic URL.
Now let’s take a look at the question in Google’s API demo.
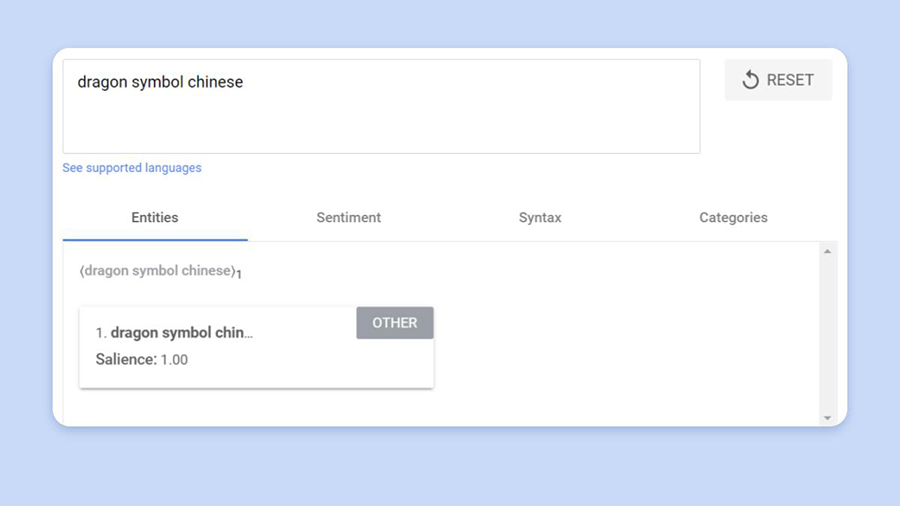



Right here we see that Google (in line with this instrument) understands the question as one entity. China shouldn’t be seen as a location as we noticed within the earlier question.
Now out of full curiosity, I modified the phrase order to ‘Chinese language dragon image’ to see if I bought the identical outcome. Within the screenshot under, you’ll see that once I change the phrase order, the phrase ‘Chinese language’ shouldn’t be seen as an entity in any respect.
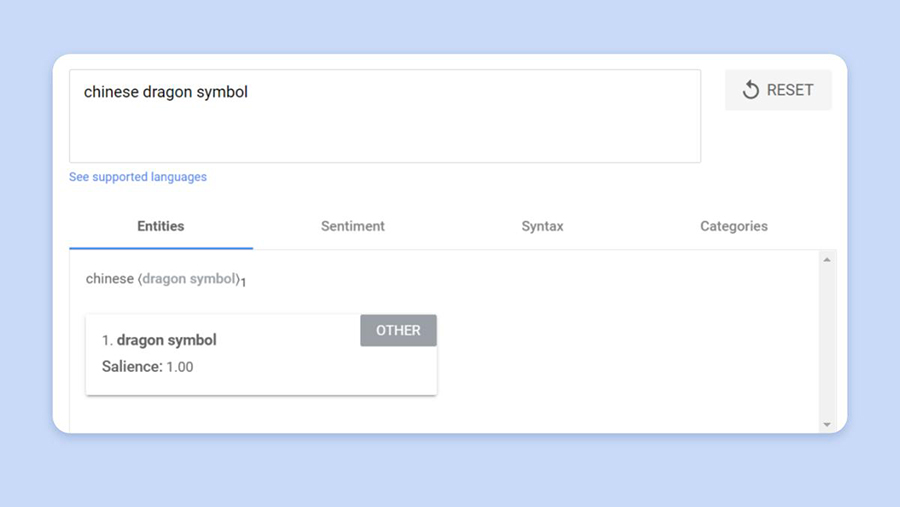



As an alternative, Google views it as an adjective.
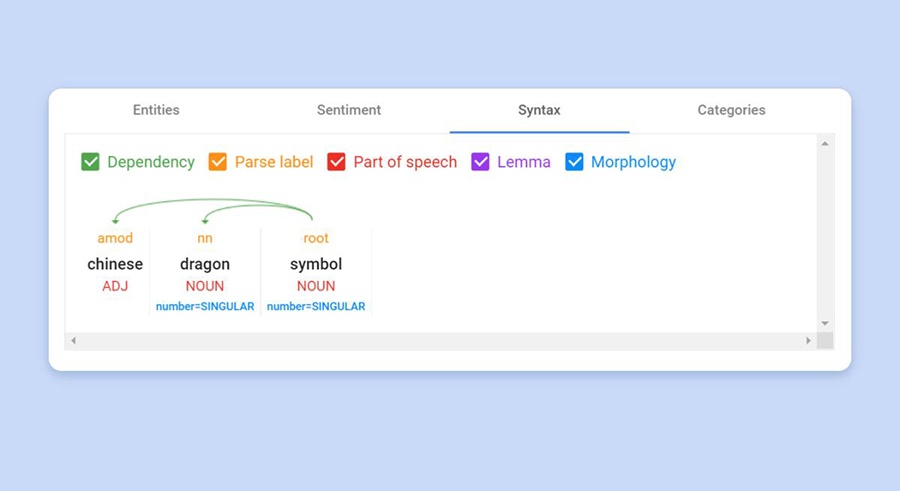



The takeaway right here is by simply altering the phrase order, adjustments how the search engine understands the question.
That mentioned, the result’s considerably satisfying however my feeling is the earlier outcome is much better.
Let’s take a look at the third question.
3. Instance #3 – ‘What’s the dragon image Chinese language’
The question ‘what’s the dragon image Chinese language’ is a mix of the earlier two queries.
Now from a person perspective, I’d think about that Google reads this question the identical approach it reads the earlier one. I imply as a human being, I learn ‘dragon image Chinese language’ as a shorthand approach of writing the sentence ‘What’s the dragon image Chinese language’.
However, should you take a look at the Featured Snippet, you’ll discover that Google doesn’t agree.




As you possibly can see from the screenshot above, Google presents the location Chineasy.com’s URL within the Featured Snippet whereas the earlier question introduced a URL from Wikipedia.
That is nearly equivalent to the Featured Snippet we noticed within the first question, which leads me to consider that the URL change within the second question was not a results of the phrase order change, however was a results of the lacking context phrases ‘What’s the…’.
If we take a look at the question utilizing Google’s NLP analyzer, we see that Google assumes that the primary entity is ‘image Chinese language’.
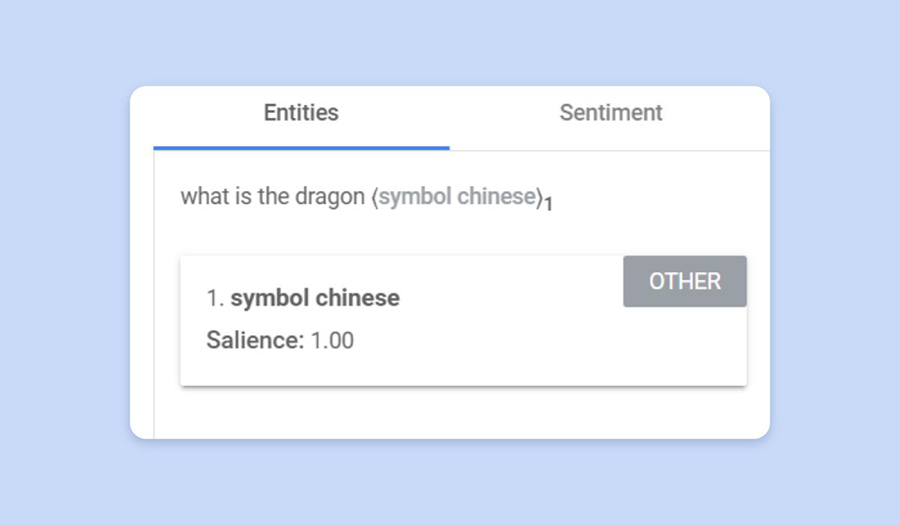



Now let’s take a look at the question ‘What does the Chinese language Dragon characterize?’
4. Instance #4 – ‘What Does the Chinese language Dragon Signify’
Once more if you take a look at the Featured Snippet, you’ll discover that Google brings you a very completely different URL. This time Google brings you depts.washington.edu.



Now, let’s attempt to perceive why Google introduced a distinct URL this time. If we examine it to the primary question ‘What’s the Chinese language dragon image’, there’s one fundamental distinction.
The primary question requested a obscure query. Whenever you ask a query beginning with ‘What’s…?’ you aren’t qualifying your query in any approach. However, if you ask the query ‘What does x characterize?’ you might be asking a extra particular query. The extra particular the query, the extra particular the reply.
Now with that in thoughts, let’s take a look at the Featured Snippet textual content.



As you possibly can see the textual content consists of the phrases ‘the dragon image represents’.
Maybe Google used this URL as a result of the question included the phrase ‘characterize’ (What does the Chinese language dragon image characterize?)
Okay, we’ve coated some NLP theories and likewise some examples of NLP in motion.
Now let’s take a look at NLP for search engine optimisation.
How Can You Implement NLP in Your search engine optimisation?
After my little demonstration, you’ve seen how Google and different search engines like google and yahoo use NLP strategies to grasp your content material. In order an search engine optimisation, the massive query is, how will you use NLP to enhance your search engine optimisation?
Beneath is a brief listing designed that will help you enhance your search engine optimisation NLP.
Embody Search Intent in Your Key phrase Analysis
As I discussed above, Google analyzes your search queries. When Google does this, it’s trying to grasp the search intent behind the question in order that it may possibly carry related outcomes that adequately reply the query.
This implies understanding how Google interprets search intent is essential. The only approach to try this is to investigate the SERPs.
The reason being, that by performing SERP evaluation you possibly can simply see what sources Google brings to reply the question. By seeing this you possibly can work out how Google understands the search intent.
Write Merely and Clearly
As you’ve seen from the NLP examples above, Google analyzes the topics and objects of sentences in your content material to determine entities. What’s extra, making small adjustments to your sentence construction can change the semantic construction of a sentence in a approach that you simply as an individual won’t detect. Keep in mind, Google isn’t human and doesn’t perceive your content material the best way that you simply do.
So, to cope with this, all the time write easy sentences and attempt to categorical one concept per sentence.
Establish and Embody Entities In Your Content material
Since Google not solely identifies entities in your content material but additionally hyperlinks entities in your content material to recognized entities in its information graph, you must attempt to determine all of the entities that Google expects to see in content material that solutions the search question.
You’ll be able to simply do that by analyzing Google’s prime content material utilizing Google’s API demo or by importing entity knowledge utilizing Python.
Analyzing your competitor’s content material with Google’s API demo is a good place to get began. Merely drop their content material into the demo and hit analyze.



When you’ve completed that, look by the Entities report. Wherever the instrument brings a URL (often from Wikipedia) you’ve discovered a recognized entity.
Utilizing this instrument, you possibly can take a look at the entire prime content material and search for widespread entities to incorporate in your content material.
Another choice is to make use of Python to seek out entity knowledge. If you wish to see how to do that, try Marco Giordano’s weblog publish on how you can use Python for NLP and semantic search engine optimisation.
Match Solutions With Questions
In an article that I noticed on Invoice Slawski’s web site, a Google patent states that your content material is extra more likely to be chosen for Individuals Additionally Ask solutions if it’s introduced as a query and reply.
In different phrases, to get your content material featured within the Individuals Additionally Ask characteristic, embrace the query in your content material after which reply it. I’d add to make it straightforward for Google to grasp that you’re answering the query, reply it instantly after the query.
Now if writing out the query and answering it instantly in your content material helps Google to incorporate your content material in PAA bins, it stands to purpose that to ensure that Google to grasp your content material, you must typically purpose to construction your content material this fashion, even in case you are not focusing on PAA bins.
Use a Clear Construction
So as to perceive entities, Google can pull data from structured and semi-structured data. This implies Google understands easy HTML markup akin to headings (H1, H2, and many others.).
What’s extra, from what I’ve seen, it’s simpler for Google to grasp structured and semi-structured knowledge than it’s for Google to grasp unstructured knowledge.
Understanding this, you must create a transparent construction in your content material utilizing logical headings (H1, H2, and many others).
(For extra readability on this, try my article on Google’s Information Graph.)
What Google’s NLP Means to You
Semantic search is right here and from what I’m seeing, it’s right here to remain.
And, what I’m seeing is that semantic search is a sport changer for search engine optimisation. We would not see it now, however as Google double’s down on algorithms like Bert and MUM, Google’s skill to work with human language is enhancing exponentially.
This means to me that we should start to optimize our content material for these algorithms. And sure, I do perceive that this department of search engine optimisation is in its infancy, however as now we have completed up to now, with somewhat trial and error, you may get a deal with on how you can enhance your site visitors and visibility.
And that was what my little experiment was all about. I’m trying to determine virtually how semantic search algorithms have an effect on search outcomes so as to work out how one can higher optimize your content material.
#NLP #search engine optimisation #work